Climate Change Countermeasures
Initiatives Related to the TCFD Recommendations
In April 2022, the Nidec Group announced its support for the TCFD recommendations. Through scenario analysis, we will grasp the possible financial impact of climate-related risks and opportunities and incorporate them into our management strategies. By doing so, we will further enhance our efforts to realize a carbon-free society.

Governance
Supervisory System
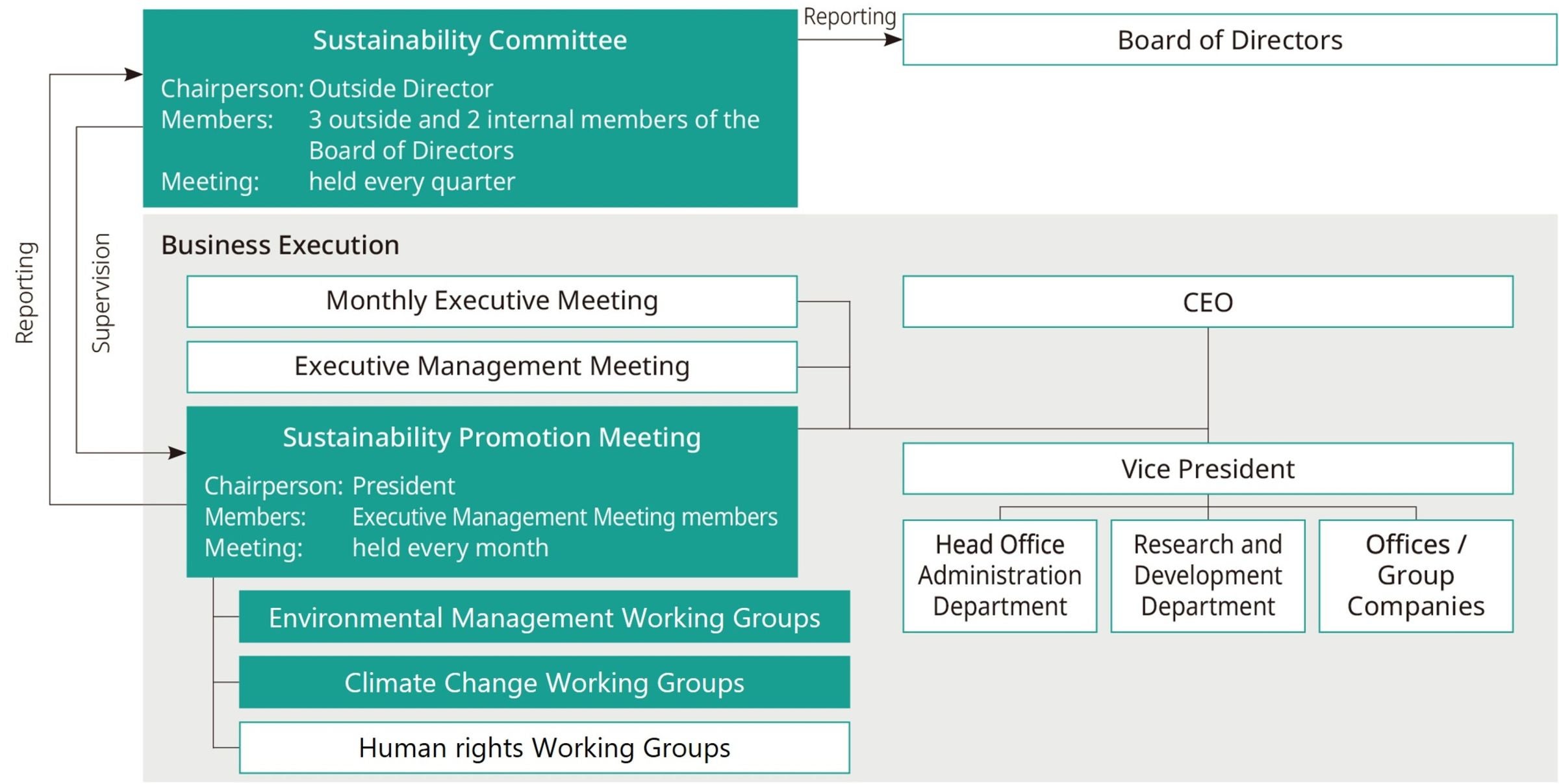
The NIDEC Group supervises the execution of sustainability-related operations and reports to the Board of Directors’ Meeting at the Sustainability Committee, which is held once a quarter. This committee is chaired by an outside member of the Board of Directors and consists of two internal directors and three outside members of the Board of Directors.
Business execution system
At the NIDEC Group’s Sustainability Promotion Meeting, the status of business execution related to material issues (materiality) including the environment is confirmed, and the sustainability activity policy and important matters are deliberated and resolved. This meeting is chaired by the president and consists of members of the Executive Management Meeting. In addition, the Environmental Management Subcommittee and the Climate Change Subcommittee have been established under the Sustainability Promotion Meeting to promote environmental initiatives across the NIDEC Group.
Sustainability promotion system
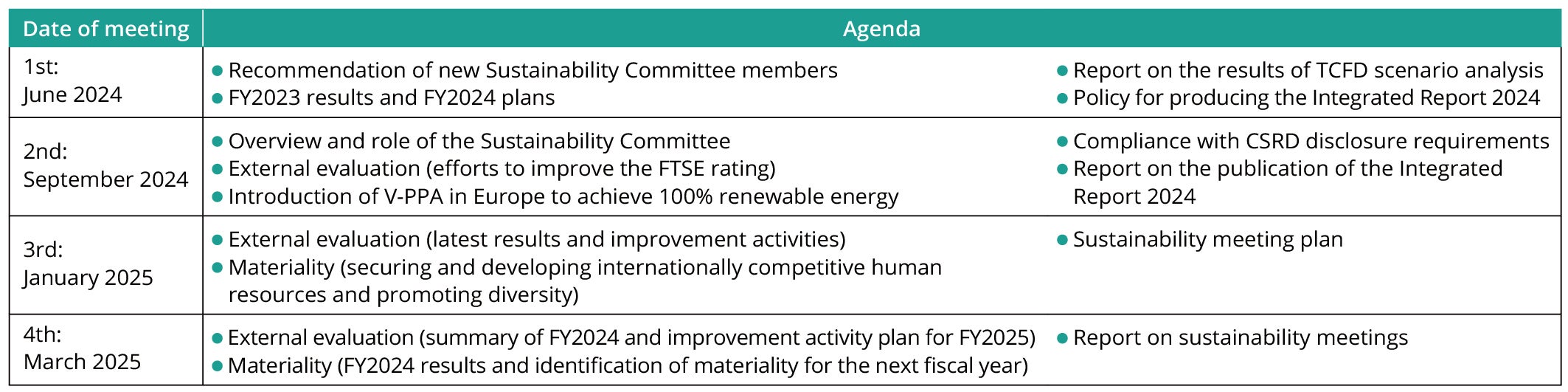
Sustainability Committee agenda in FY2024
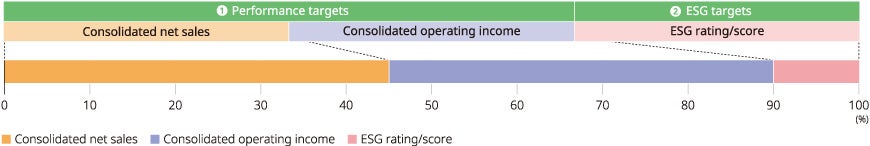
Reflecting ESG targets in performance-linked compensation for directors
From 2024, a performance-linked coefficient will be incorporated into the performance-linked share-based remuneration for directors (excluding the Founder and Chairman of the Board, outside members of the Board of Directors, and directors who are members of the Audit, etc. Committee) in accordance with the degree of achievement of performance targets in a single fiscal year, etc. The degree of achievement of ESG targets will be determined based on the ESG rating or score of the Company by MSCI, FTSE, and CDP, and will be reflected in the performance-linked coefficient.
Evaluation indicators and weights for performance-linked coefficients
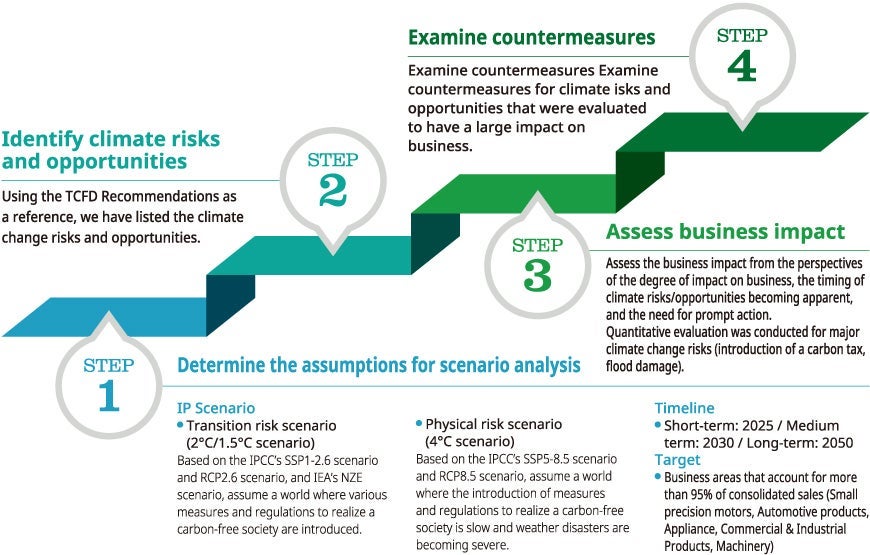
Strategy
A total of 143 executives and managers from the business areas that account for more than 95% of our consolidated sales (Small precision motors, Automotive products, Appliance, Commercial & Industrial
Products, Machinery) conducted scenario analysis according to the following procedure to identify climate change risks and opportunities with a significant impact on our business, and to consider
countermeasures.
The results of the scenario analysis were reported to the general managers of each business division, the Sustainability Promotion Meeting, and the Sustainability Committee.


Steps of scenario analysis
Specific examples of countermeasures
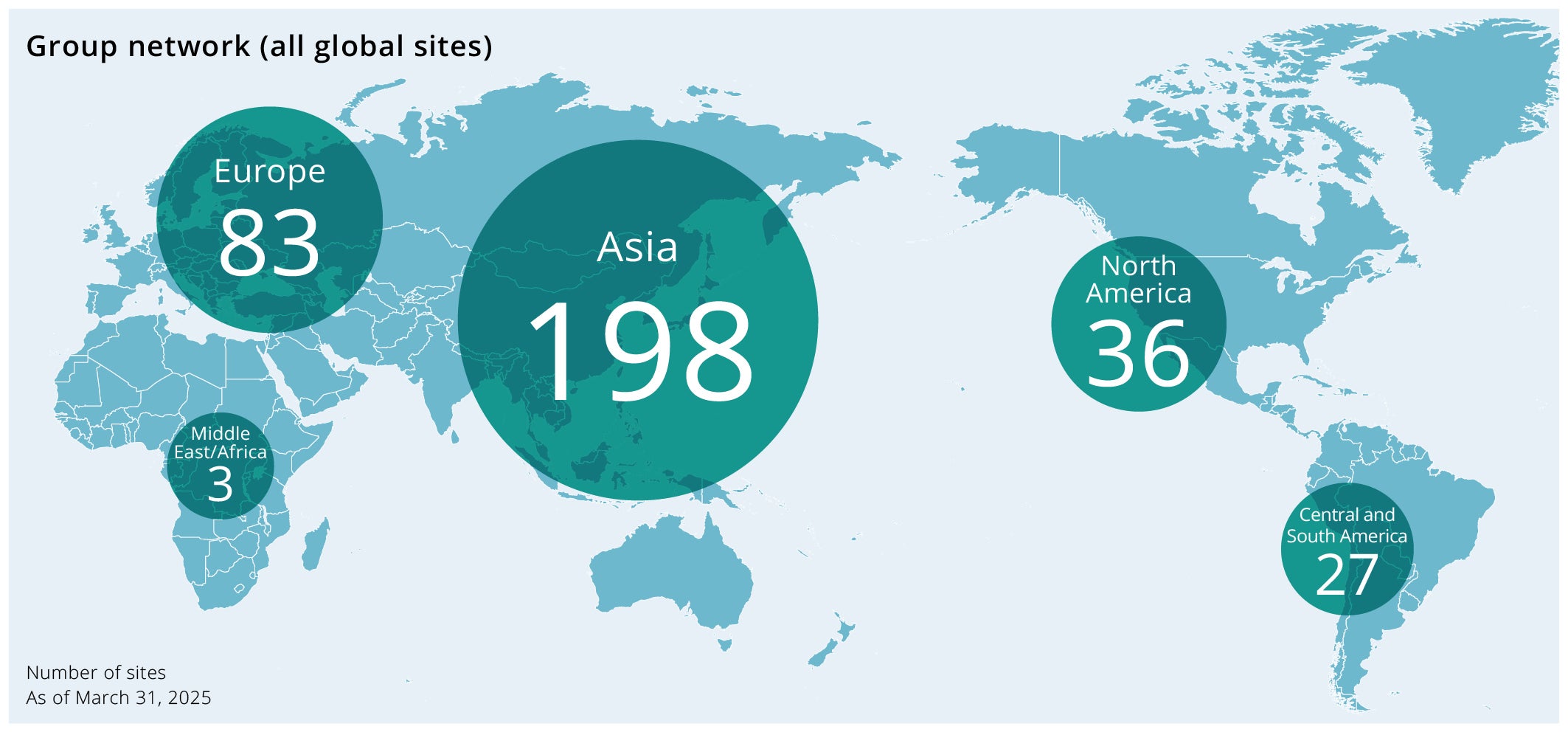
Geographical distribution of production plants
Nidec has a group network covering over 300 companies in more than 40 countries around the world and aims to reduce geopolitical risks and climate-related physical risks by geographically distributing its operation sites.
Introduction of an internal carbon pricing system
In September 2025, we introduced an internal carbon pricing (ICP) system to incorporate the costs of carbon emissions into our capital investment decisions. The internal carbon price was set at 20,000 yen/t-CO₂ with reference to the reports published by the International Energy Agency (IEA), and will be revised as appropriate in response to changes in the external environment. We will accelerate our efforts to combat climate change by promoting capital investments that contribute to decarbonization.
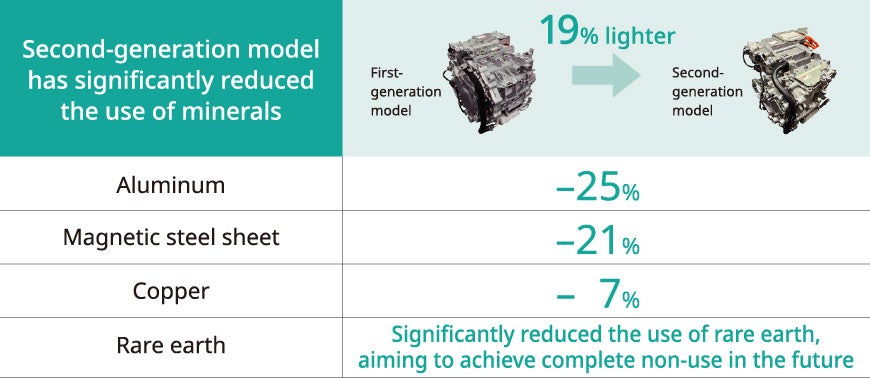
Reduction of size and weight, and resource saving by employing the “light, thin, short, and small” technology
Nidec manufactures socially and environmentally conscious products by making motors smaller and lighter and resource-saving. The first-generation model (Gen.1) of our EV traction motor system (E-Axle) achieved an overwhelming miniaturization of the motor by employing “light, thin, short, and small” technology and the oil cooling structure we had cultivated in the small precision motor business. The second generation (Gen.2) E-Axle, which began mass production in September 2022, achieved a 19% reduction in weight compared to Gen.1 thanks to the use of smaller magnetic circuits and inverters, based on the high-space-factor wire-winding technology, and also a substantial reduction in the amount of minerals used. In addition, the newly developed two-way oil-circulation system has improved the cooling capability, making it possible to use magnets that require significantly less amounts of dysprosium (Dy), terbium (Tb), and other kinds of heavy rare earth. Moving forward, we are planning to develop motors that do not use heavy rare earth or magnets.
Climate-related risks and opportunities with significant business impacts, and their countermeasures
| Impacts of climate-related risks and opportunities | Countermeasures |
Small precision
motors |
Automotive
products |
Appliance, Commercial &
Industrial Products |
Machinery | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPMS | AMEC | ACIM | MOEN | NMAB | |||||
|
Transition
risks |
Policies and
legal regulations |
Introduction of carbon
taxes |
|
|
〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | |
|
|
〇 | 〇 | ||||||
|
|
〇 | 〇 | ||||||
|
|
〇 | 〇 | ||||||
|
Tightening of regulations
for fuel efficiency and ZEVs |
|
|
〇 | ||||||
|
|
〇 | 〇 | 〇 | |||||
|
|
〇 | 〇 | ||||||
|
Introduction of regulations
related to rare earths |
|
|
〇 | 〇 | |||||
| Technologies | Impact on R&D capabilities |
|
|
〇 | |||||
|
Failure in investment in
new technologies |
|
|
〇 | ||||||
|
Transition to low-carbon
technology |
|
|
〇 | ||||||
| Market |
Changes in customer
behavior |
|
|
〇 | 〇 | 〇 | |||
|
Rise in raw material costs,
difficulty in obtaining raw materials |
|
|
〇 | 〇 | |||||
| Reputation |
Changes in investor
evaluations |
|
|
〇 | 〇 | ||||
| Physical risks | Acute |
Impact of floods,
submergence, torrential rain or typhoons |
|
|
〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | |
| Chronic |
Impact of droughts, water
shortage, and changes in the precipitation pattern |
|
|
〇 | 〇 | ||||
| Opportunities |
Products/
services |
Expansion of the
market for products that contribute to decarbonization |
|
|
〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 |
|
Market expansion for
products that counteract temperature differences |
|
〇 | 〇 | ||||||
| Market | Expansion of EV market |
|
〇 | 〇 | 〇 | ||||
| Progress of electrification |
|
〇 | |||||||
|
Entry into new markets
with new products |
|
〇 | |||||||
| Resilience | Strengthening the supply chain |
|
|
〇 | |||||
Quantitative evaluation of business impact
| Risk | Financial impact | Calculation method |
|---|---|---|
| Introduction of a carbon tax | 12.4 billion yen | The carbon price is based on the IEA’s “World Energy Outlook 2022” forecast of 140 USD/t-CO₂ for developed countries in fiscal year 2030. We calculate 610,000 t-CO₂ based on our Scope 1 and 2 emissions reduction targets for fiscal year 2030. |
| Flood damage | 7.7 billion yen |
Based on risks assessment using the World Resources Institute’s water risk analysis tool “Aqueduct”, sales, and status of business continuity plan (BCP) among other factors, we assessed
business impact of the case where all of the five sites assessed to have high flood risks are flooded.
We used as reference the “guidelines on physical risk assessment based on the TCFD recommendations” issued by Japan’s Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism to calculate the financial impact of lost opportunities caused by damaged fixed assets and inventory and by the suspension of business operations. |
From now on, we will work to improve the quality of our business impact assessments, and promote initiatives to effectively reduce climate change risks effectively.
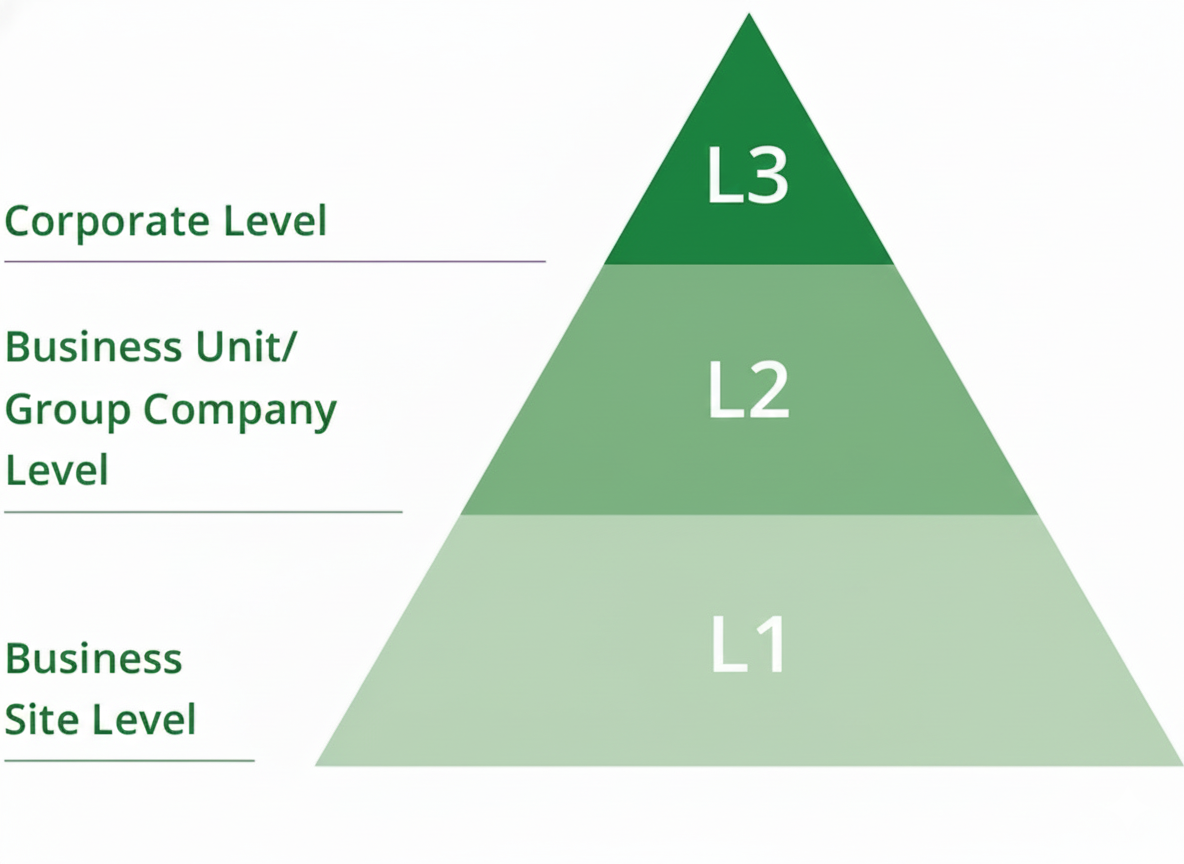
Risk management
We established a framework in which risk surveys are conducted for each of the levels illustrated below and the survey results are shared and mutually used.
With risk managers in place at each of our global locations, we are working to detect and respond appropriately to factors that could hinder business continuity. We are focusing on comprehensively understanding and mitigating climate change risks through measures that focus on compliance with increasingly strict climate change-related laws and regulations, adapting to changing market trends, and strengthening communication with customers, investors, and other stakeholders, while also conducting BCP simulation training at our sites in Japan and overseas, assuming the occurrence of risks such as floods and droughts.
Indicators and targets
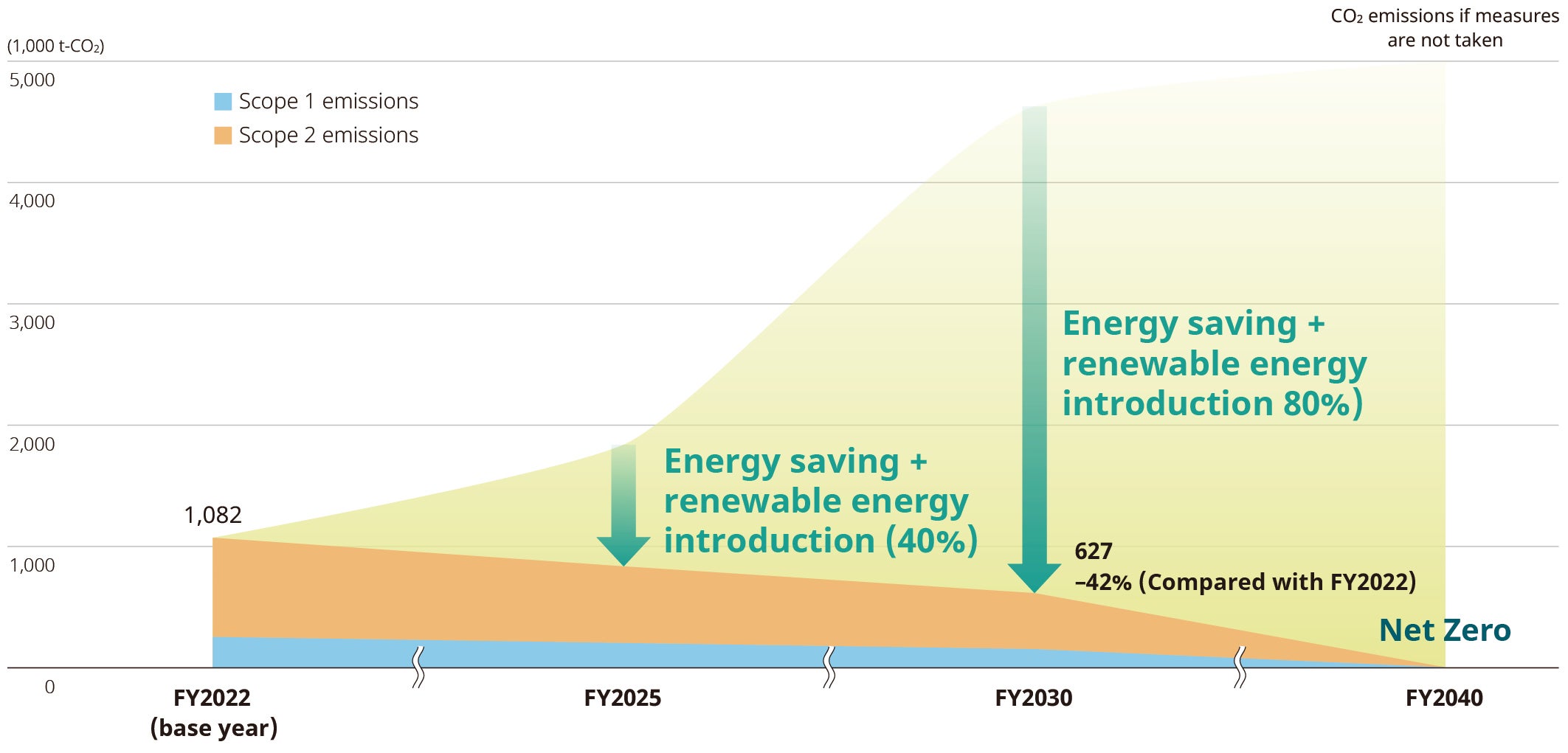
As one of the major axes of ESG materiality measures, the NIDEC Group aims to achieve net zero CO₂ emissions by fiscal year 2040. In fiscal year 2023, we underwent third-party verification of our CO₂ emissions and formulated CO₂ reduction targets for fiscal year 2030 in line with the guidelines. This target was recognized as a scientifically based target for achieving the “1.5°C target” in the Paris Agreement, and we have obtained SBT certification.

Scope 1 and 2 emissions reduction targets
Scope 3 emissions reduction target
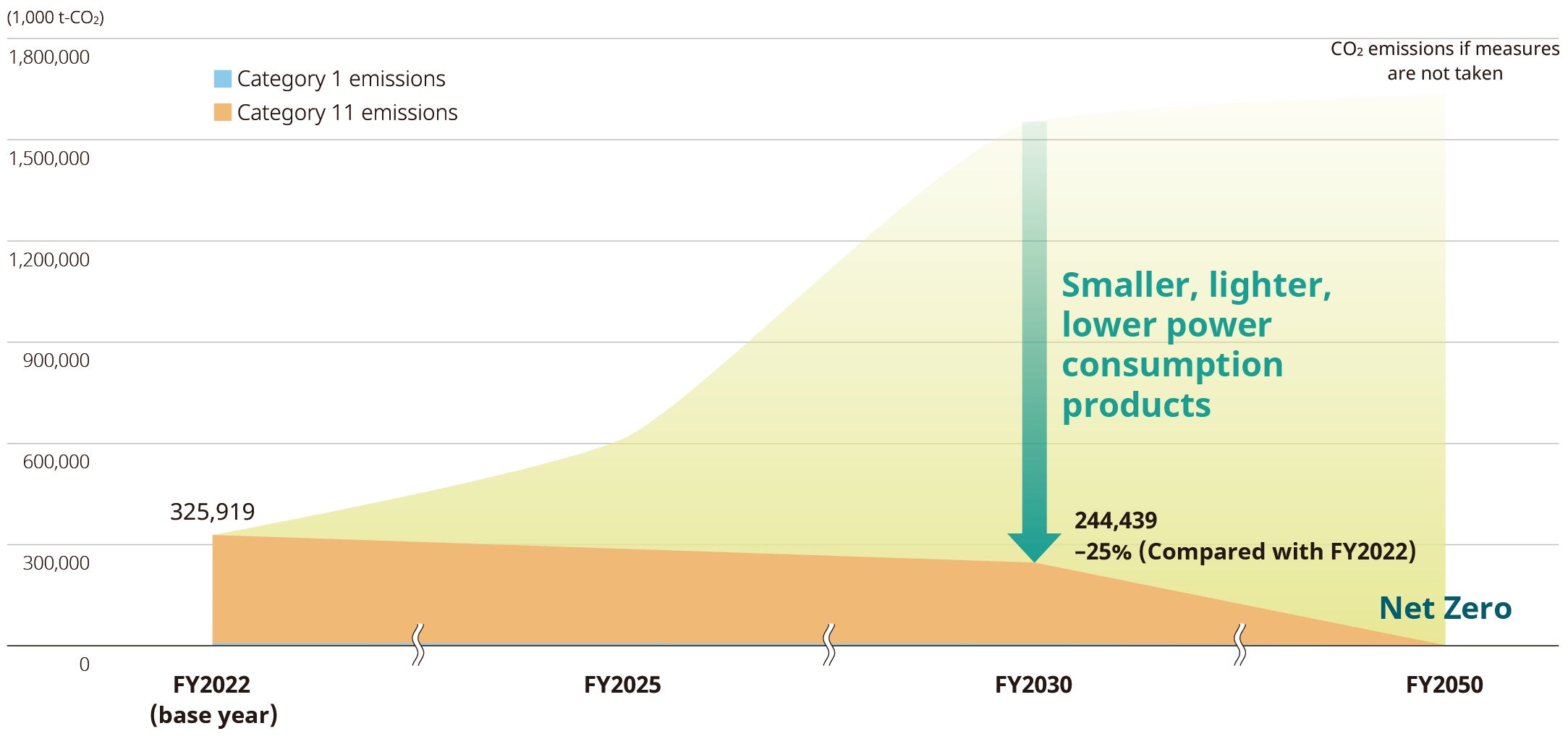
In addition, we have identified “contributing to a sustainable global environment” as one of our materiality issues, and have set the following targets.

