Glossary of Motor Terms
RMS (Root-mean square) value
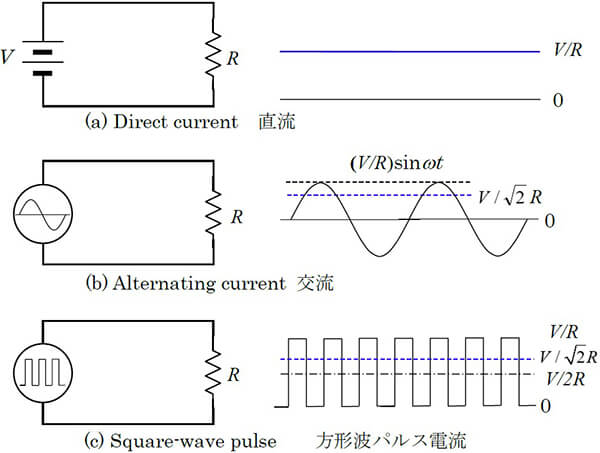
In Fig. (a), the resistor R is connected as the load of the DC power
supply of the voltage, V. The current in this circuit is V / R, and the power consumed by the power supply is V2 / R.
Fig. (b) shows the case of a simple AC power supply Vsin ωt. The current also changes with time and is expressed by (V/R)sinωt. In addition,
the power consumption also varies with time and is represented by the function (1-cos 2ωt)/2. On average, it is (1/2) V2 / R, and when this is converted to the case of the DC in
(a), the voltage corresponds to the direct current of V / √2.
This voltage is the root-mean square value.
Fig. (c) shows the case of square wave voltage. When voltage V and a
voltage of 0 are applied at equal intervals, the average power consumption is (1/2) V2 / R as in (b). In
this case as well, the effective (root-mean square) voltage converted into DC is V / √2. However, the time average of this square wave is V/2. Thus, the average voltage and the root-mean square value voltage are
different.
Term List (R)
- Rare earth magnet
- Reactive power
- Rectification via commutator
- Regenerative brake
- Reluctance motor
- Remanence,Remanent magnetization
- Resolver
- Reversible motor
- Revolutions per minute (rpm)
- Revolutions per second (rps)
- Revolving field (Rotating field)
- Revolving field motor
- Right-hand screw law
- Ring spring
- Riser
- RMS (Root-mean square) value
- Rotor, Stator
- Rotor cross-sectional structures
