Glossary of Motor Terms
Coupling,Rigid coupling
A coupling is a device used to connect two shafts together at their ends for the purpose of transmitting power,
torque, or motion. The primary purpose of couplings is to join two pieces of rotating equipment while permitting
some degree of misalignment or end movement or both.
Couplings are commonly used to join the shaft of the motor to that of the driven load.
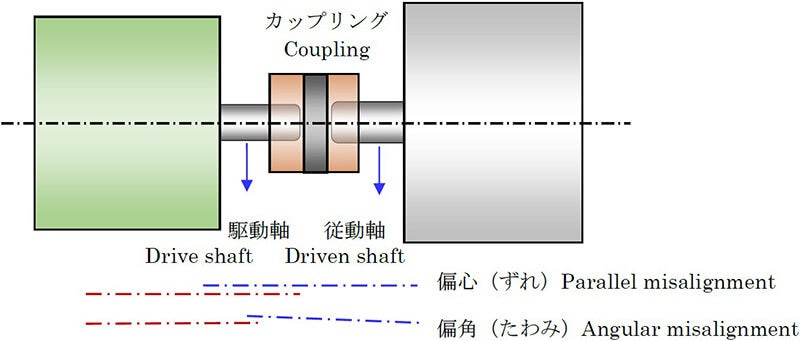
Rigid couplings, also called muff or sleeve couplings, consist of cylindrical sleeves, such as the one shown in
Fig. (a), and are the simplest type of coupling. However, they are not used very often because the shafts of the
motor and driven load must be axially aligned and kept parallel accurately. Couplings for small motors with
outputs of several hundred watts are usually made from aluminum rods or aluminum die-castings, although zinc
die-castings and fiber-reinforced engineering plastics are used as well. Meanwhile, large couplings are usually
made from steel or cast steel. Flexible couplings often use elastomeric inserts, of spring steel plates or
rubber, to absorb axial misalignment (eccentricity) or angular misalignment (declination).

Term List (C)
- Capacitor-run motor, Capacitor-start motor
- Carbon brush, Graphite brush, Metallic graphite brush
- Circulating current
- Coercive force, coercive intensity
- Cogging torque
- Commutation
- Commutator, Commutator segment
- Concave and Convex
- Concentrated winding
- Concentric winding
- Concentricity, Eccentricity
- Conductor
- Consequent pole
- Constant-power characteristics
- Construction of a DC motor
- Continuity of magnetic fields
- Cooling methods
- Copper machine, iron machine
- Core, Iron core, Laminated core, Lamination
- Coreless motor
- Coulomb friction
- Coupling,Rigid coupling
- Cylindrical motor
